Five critical bills on the Governor’s desk
Please urge Governor Newsom to sign them
***September 30, 2024 Update – Governor Newsom has signed AB 2245 and vetoed AB 2088, AB 2277, AB 2586, and SB 1182**
Five critical pieces of legislation are on the Governor’s desk. Please take a moment to sign the letters below, urging him to sign these important bills.
Local bargaining for part-time faculty healthcare ramps up
Phase 2 of Part-Time Faculty Campaign kicks off with regional meetings, negotiations training, Campus Equity Week
Securing annual funding for part-time faculty healthcare is an unprecedented legislative win. The next step is to secure that healthcare at the local bargaining table.
Legislative high and low for part-time faculty
Healthcare funding increased in state budget, but higher workload cap vetoed
California community college adjuncts saw the single greatest gain for part-time faculty ever—$200 million in ongoing annual funding for part-time faculty healthcare—but felt bitter disappointment when CFT’s sponsored bill to lift the teaching cap to 85% of a full-time load died for a second time on Governor Newsom’s desk.
AFT resolution asks U.S. Department of Education to conduct higher ed study
Calls for national data about adjunct/contingent pay and benefit inequities
CFT once again demonstrated its commitment to adjunct/contingent faculty by submitting and winning unanimous passage of its resolution “Calling for Department of Education Study of Pay and Benefit Inequity” at the AFT Convention July 15 in Boston.
FAQ: Part-time faculty healthcare, collective bargaining & state budget
Answers to common questions
Updated September 27, 2022
This year we won a historic expansion of state funding for part-time community college faculty healthcare, increasing state support from $490,000 to $200 million in ongoing funding.
The funding will enable local community colleges to provide quality, affordable, and accessible healthcare to substantially more part-time faculty. Local unions should now prepare to go to the bargaining table to negotiate the healthcare implementation.
Join a campaign kickoff meeting on Zoom — Faculty Healthcare Now!
In phase 2, learn how to secure funding for part-timer healthcare in your community college district
We invite local union leaders, activists, and rank-and-file members to please join us and kick off this phase with faculty power!
In Phase 1 of the Part-Time Faculty Campaign, our collective efforts secured $200 million in ongoing funding for part-time faculty healthcare in the California state budget. Now in Phase 2, we are launching coordinated collective bargaining as members begin to mobilize and bargain in their home districts to secure this funding in contracts or MOUs.
Urge governor to increase workload cap for part-time faculty
Ask Governor Newsom to sign CFT-sponsored bill to raise the cap to 85%!
UPDATE: We are disappointed to report Governor Newsom vetoed AB 1856 on September 25, citing cost concerns. Find his veto message here. This action is now closed.
Please take a moment to urge Governor Newsom to sign AB 1856, which will increase the workload cap available to part-time faculty from 67% up to 85% of a full-time faculty workload in California’s community colleges.
Join a campaign kickoff meeting this fall — Faculty Healthcare Now!
Local mobilizing and bargaining — learn how to secure funding for part-time healthcare in your community college district
In phase one of the Part-Time Faculty Campaign, our collective efforts secured $200 million in ongoing funding for part-time faculty healthcare in the California state budget.
Now we are launching phase two — coordinated collective bargaining — as members begin to mobilize and bargain in their home districts to secure this funding locally.
FAQ: Part-time faculty healthcare, the state budget, and collective bargaining
Quick answers to common questions
Updated July 1, 2022
About half of the California community college districts offer healthcare benefits for part-time faculty; the quality of the benefits is wide ranging with some offering the same benefits package to full- and part-time faculty and some offering very modest stipends to help cover the cost of insurance.
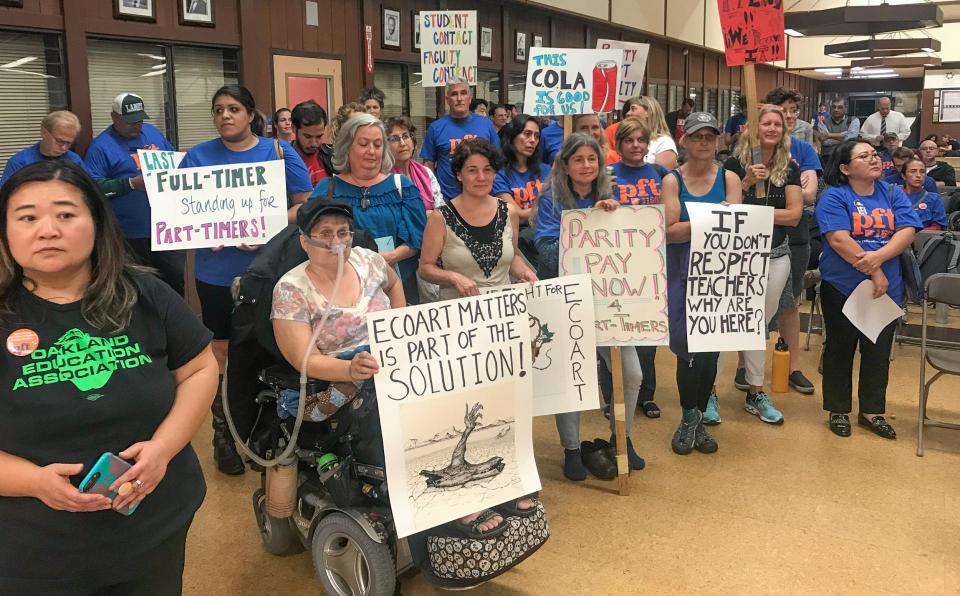
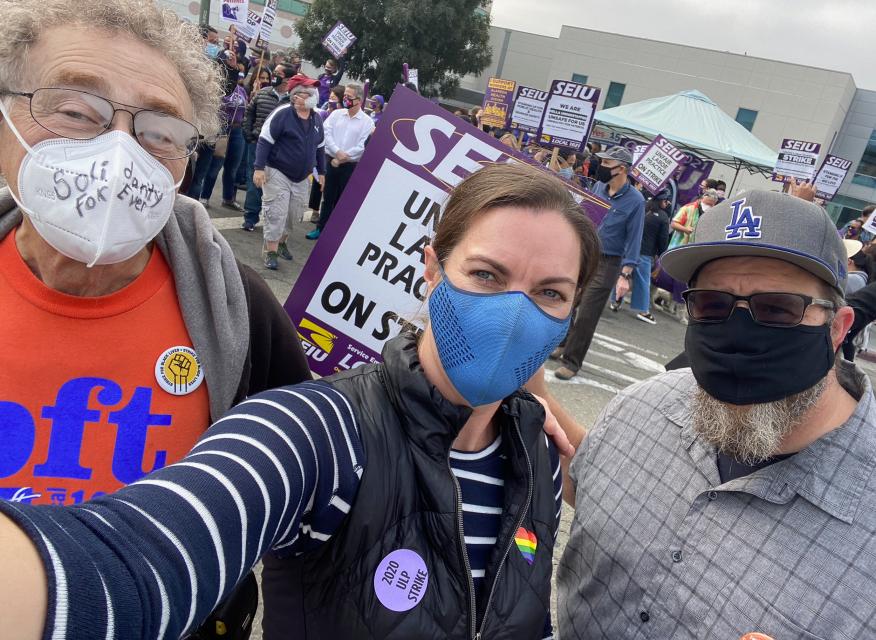
Part-timers and allies lobby legislators for healthcare, pay parity
PHOTO GALLERY
Students and full-time faculty join forces with part-time faculty
From the Bay Area to San Diego, and from the Central Valley to the Mojave Desert, part-time community college faculty, along with full-time faculty and student allies, gathered at Sacramento’s famed Sutter Club on Monday morning, May 1, to go forth and make California legislators aware of the critical need for part-time faculty healthcare and pay parity.
Part-Time Faculty Conference empowers through learning
PHOTO GALLERY
Workshops focus on bargaining, lobbying, organizing, diversity, communications
When it comes to union work, power and knowledge work hand in hand. Union is not simply about expressing demands, speaking truth to power, and being resolute in the face of adversity. It’s about making connections, sharing truths, building solidarity, empowering, and speaking to be heard.
Developing the knowledge to do these things and putting the power of that knowledge to use was core to the workshops at the CFT Part-Time Faculty Conference held May 1-2 in Sacramento.
Groundbreaking CFT survey calls out healthcare crisis among part-time faculty
Critical insights into part-time faculty in community colleges statewide
The results of CFT’s groundbreaking statewide survey of part-time faculty offer critical insights into the daily, personal, and structural challenges that part-time and contingent faculty experience when it comes to healthcare.
A “red letter year” for CFT legislation in support of contingent faculty
Healthcare insurance, teaching load, rehire rights, and parity
COVID and the subsequent student enrollment drop during the last two semesters have placed great burdens on contingent faculty, from scrambling to teach remotely to negotiating personal and family challenges to facing reduced assignments and a loss of healthcare benefits.
Continued enrollment woes create challenges for part-time faculty
Local unions finding solutions in pandemic-driven tough times
While California is showing strong signs of emerging from an economy ravaged by the pandemic, the community colleges are still reeling from the impact, most strongly demonstrated in the sharp decline in student enrollment. This has led to tough situations for many adjuncts, and for the local unions representing them.
HELU Winter Summit unites efforts across unions
Promotes socio-economic and racial justice in higher education
HELU, or Higher Education Labor United, a cross-union and cross-sector coalition, held its Winter Summit virtually on February 23-27, pushing forward with the larger goals of reclaiming the promise of higher education, and promoting socio-economic and racial justice embodied by the New Deal for Higher Education campaign and Scholars for a New Deal in Higher Education.
New AFT report shows pandemic wreaked havoc on nation’s adjunct faculty
Transition to remote learning, impact of virus lead to declines in job security, increased reliance on public assistance
WASHINGTON — A new national adjunct faculty survey from the AFT underlines the brutal economic reality faced by millions of contingent and adjunct faculty at the nation’s colleges and universities — and illustrates how the pandemic further eroded job security and bolstered the need for public help.
Part-time faculty step up to win the healthcare they deserve
Dozens of faculty testify before state legislative committees
Dozens of CFT members testified this week in front of two different budget subcommittees of the California Legislature to urge our elected leaders in Sacramento to support Governor Newsom’s $200 million proposal in the state budget to fund healthcare for part-time faculty in California’s community colleges.
Following the launch of CFT’s campaign for part-time faculty healthcare last fall and a successful letter campaign, the governor included the $200 million in his January budget proposal.
UC lecturers’ victory inspires broad movement for equity across higher education
CFT wages a campaign for part-time faculty in the community colleges
By Jeffery M. Freitas, CFT President
For about three years the University Council-AFT engaged in protracted negotiations on behalf of lecturers in their unit. Their aims have always been about fairness — better working conditions for lecturers and improved learning conditions for students. Their fight has been about not only winning economic and contractual gains for members, but gaining professional respect and recognition for their teaching at the University of California. Their campaign has been a true member-driven effort, rooted in years of organizing by the statewide local that represents both continuing lecturers and librarians, led by their president, Mia McIver, and a committed negotiations team.
Part-time faculty face loss of work, health benefits in COVID times
Locals negotiate vaccine stipends, reduced class minimums, retention of health benefits
As the COVID pandemic stretches into the fall, community college adjuncts have been hit especially hard by the decline in student enrollment, limited support services, and inadequate or even non-existent access to healthcare. The loss of work, loss of insurance benefits, and even the breakdown of personally financed yet essential teaching equipment have been the tragic results.
CFT launches campaign to secure healthcare for part-time faculty
“Adjuncts deserve, at the very least, the basic right of healthcare”
The pandemic has pushed many harsh realities in higher education to the forefront, none more so than the inadequacy of healthcare for part-time faculty. With the cost of an average COVID hospitalization, according to a number of sources, running in excess of $20,000, the financial effects alone on an uninsured part-timer contracting COVID can be devastating. Add a possible uninsured family member or members to the mix, and the reality becomes even more frightening.
“Power Despite Precarity” — how contingent faculty can build greater solidarity and success
BOOK REVIEW
Power Despite Precarity: Strategies for the Contingent
Faculty Movement in Higher Education
By Joe Berry and Helena Worthen
Pluto Press, 2021
Reviewed by Geoff Johnson
If there were two words which often define what may best be termed the “contingent condition,” they would be alienation and powerlessness.
Governor’s veto of AB 375 disappointing setback in push for increased workload cap
Legislative update for part-time faculty
“Bittersweet” might be the best word to describe CFT’s legislative efforts on behalf of part-time faculty this year, with gains in categorical funding, but a last-minute veto of the union-sponsored bill to raise the teaching cap in a single community college district from 67% to 85% — AB 375.
New coalition groups take bold steps for higher ed justice
Higher Education Labor United expands labor outreach
Several months ago, when Congress began the budget reconciliation process, there were significant aspirations that the final bill would result in a significant uptick for higher education, including funding for free community college.
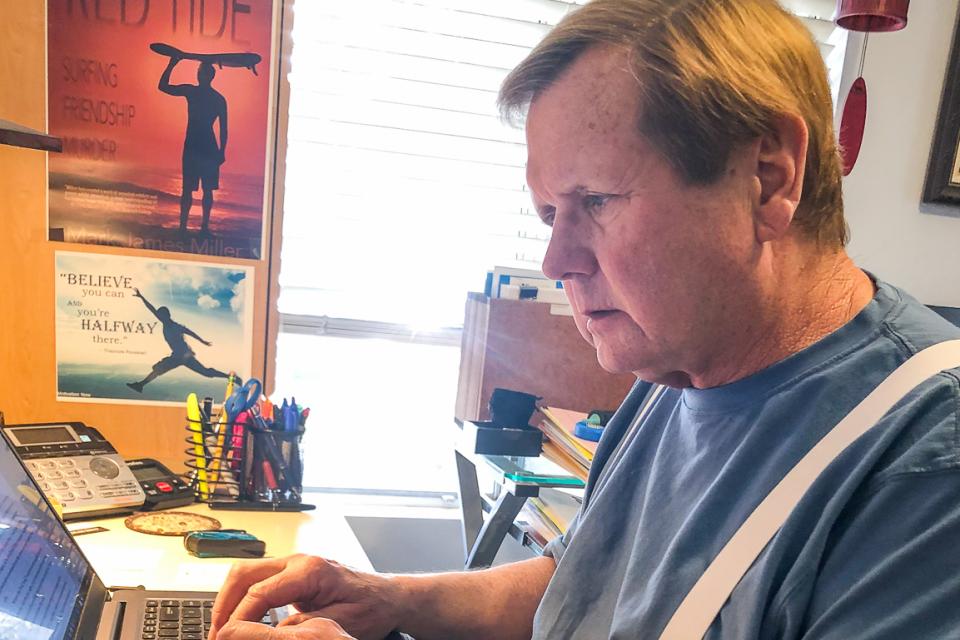
Make your passion happen — Mark James Miller pens second novel
Steadfast dedication to teaching, the union and writing
Mark James Miller’s second novel, The White Cockade, was published on September 30 to numerous advance accolades including from the Kirkus Review.
In Memoriam: Paul Baltimore and Ken Taira
Unions lose faculty dedicated to part-timer activism
It is vital in what has been the long struggle for part-time equity and social justice that we fully acknowledge those activists who up until their passing, gave their all and inspired many. Two such figures are Paul Baltimore and Ken Taira. Both members were recognized at CFT State Council on September 25.
Governor signs three CFT-sponsored bills, vetoes AB 375 to increase part-time faculty workload
Legislative Update
The governor signed three of four CFT-sponsored bills that made it to his desk in year one of the current two-year session. The session closed on September 10 and Governor Newsom had until October 10 to sign the bills.
Urge governor to increase workload cap for part-time faculty
Send a letter in support of AB 375 now!
Please take a moment to urge Governor Newsom to sign AB 375, which would formally increase the workload cap available to part-time faculty from 67% up to 85% of a full-time faculty workload in California’s community colleges.
How Peralta won the first pay parity in CA community colleges
San Mateo Federation campaign makes big strides toward parity
Equal pay for equal work. It’s a simple idea, but one that has remained all but elusive for part-time faculty, so much so that some have decried the quest for it as a Sisyphean effort. However, the recent gains made by the Peralta Federation of Teachers shows that parity is possible.
Now, Peralta pays its adjuncts at the same hourly rate for teaching and office hours as its full-time faculty — a first in the California Community College system.
Adjuncts and their unions fight on in the face of COVID
Enrollment decline, lost classes, adjunct relief fund
While the number of COVID cases are shrinking, and the vaccination rate increasing, the effects of the pandemic continue, with adjuncts having been hit particularly hard, as despite the heroic efforts of faculty to provide remote and online instruction, California community college enrollment has dropped systemwide by 11 to 12% since last fall, according to Edsource.
CFT seeks 85% adjunct teaching load, statewide path to pay parity
Union-sponsored legislation tackles long-standing adjunct issues
After last year’s heavily pandemic-impacted legislative session reduced the number of bills signed to its lowest number since 1967, the CFT is again taking up the adjunct cause on bills directed towards raising the part-time percentage cap on teaching in a single district, and in developing a path towards part-time/full-time pay parity.
Healthcare, transferable training top adjunct priorities at CFT Convention
Delegates resolve to address timely adjunct issues
At this year’s virtual CFT Convention held March 26-27, the Part-Time Faculty Committee sponsored two resolutions reflective of both the longstanding and new problems beginning to emerge in the wake of the pandemic which has impacted adjunct health and training.
Adjuncts at the table to win a New Deal for Higher Education
National campaign calls for sea change in higher ed
While the COVID-19 pandemic has amplified longstanding societal inequities in America, public higher education was already in a state of crisis, from the staggering costs of college, to the lack of access and support for lower income students, Black, indigenous, and people of color, the deteriorating, or clear lack of infrastructure, the reciprocal increase in highly paid administrative positions, and last but not least, decrease in full-time tenure track positions.
Peralta reaches 100 percent pay parity; locals win distance education support
From course conversion stipends to health benefits extensions
In spite of the pandemic, a number of local unions won big gains for adjuncts, from parity pay to distance education, to the preservation of healthcare for adjuncts with reduced loads. These wins are especially significant at this time in which revenues are falling and concerns over future budgets made many administrators skittish to bargain.
Contingent faculty team up, pass national shared governance policy
AFT Convention adopts resolution crafted by UC and community college faculty
While the COVID-19 pandemic meant that this summer’s AFT Convention had to go virtual, and in turn, resulted in format changes which made schedules tighter, and the work of those attending harder in many respects, one of the great achievements for CFT was the passage of a resolution calling for the right of contingent faculty to participate in shared governance.
The patient is on the table — Higher Education in America is sick
Opinion
By Geoff Johnson, AFT Guild, San Diego and Grossmont-Cuyamaca Community Colleges
Higher education in America is sick. Its classrooms and campuses have been largely shuttered, save but for students taking lab courses, or practicums, ironically in hospitals. Students and instructors are now confined to the domains of their computers and laptop screens in the educational netherworlds of Zoom or Cranium. With the exception of online instruction developed prior to the crisis, what is being delivered, more so than taught, is a curriculum of coping under the duress of the coronavirus pandemic.
College students staying positive through the pandemic
Union presidents surveys students for newspaper column
By Mark James Miller, Part-Time Faculty Association of Allan Hancock College
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought its own unique challenges to every facet of society. Everyone has been seriously impacted by the virus, and students in higher education are no exception.
Nationwide, students are delaying their education until the pandemic is over and colleges return to the traditional classroom approach instead of the online model being used in its place. Some are simply uncomfortable with online learning, and others are fearful that the education they receive remotely is not of the same quality as what they get in the classroom with the instructor present.
Allan Hancock College teachers and the ‘new normal’
Union presidents surveys part-time faculty for newspaper column
By Mark James Miller, Part-Time Faculty Association of Allan Hancock College
“I miss the face-to-face contact.”
“Something is missing.”
“I miss being with my students.”
As Hancock College’s part-time instructors adapt to the “new normal” brought on by the coronavirus, one theme is constant: With all classes now being taught remotely, they miss being in the classroom with their students.
Adjunct faculty leaders organize, meet challenges of pandemic
The union picture — now and in the months ahead
The ongoing COVID-19 experience for part-time instructors has demonstrated their great collective strength and resiliency, despite limited pay, benefits, job security, and often minimal support.
Several local union leaders — who are part-time faculty — report that beyond the initially hectic and at times frenzied process of transitioning to remote instruction and services, faculty have more or less still been able to teach a semblance of their face-to-face course.
Part-time faculty face the travails of remote teaching
Stories of teaching from home during the pandemic
Within the span of just two weeks in early March, California Community Colleges, along with the rest of American higher education, were forced into the perhaps the largest and most radical pedagogical shift in its history.
Relief for part-timers and their families during pandemic
Unemployment Insurance, housing, utilities, student loans
In the wake of the COVID-19 crisis, part-time faculty — beyond dealing with protecting the health and safety of themselves and their families — are facing threats to their economic security, including loss of income, access to health insurance, and their capacity to pay for housing and utilities.
It is essential part-timer faculty are aware of recent actions taken by the federal government and state of California to provide relief for people facing these challenges.
“An Army of Temps” — AFT’s call to action
New AFT report attaches numbers to the human crisis in higher education
Part of the tragedy of the COVID-19 pandemic is that for those who were already at risk, it has laid their situation bare. This is a part-timer reality.
“While it may seem like an odd time to be putting out the “Army of Temps: AFT Contingent Faculty Quality of Worklife Survey,” frankly, it’s about as good a time as ever to show the fragility of this workforce.”
Finding “common ground” in higher education
Campus Equity Week conference brings together contingent faculty from all higher ed systems
Members, officers, and activists from higher education unions throughout California came together for a full day during Campus Equity Week to chart a strategy for defending public higher education. They denounced especially the way education institutions, under corporate pressure, increasingly rely on contingent instructors while treating them as outsiders.
Part-timer takes the helm at State Center Federation of Teachers
One of the great powers of a union is its ability to uplift the living conditions and status of its members, not just at the bargaining table, but within the structure of the union itself — when the seemingly most marginalized members assume leadership roles.
In local unions representing all faculty, there has been a recent trend of the membership electing a part-time faculty member to lead the union, with significant support from the full-timers. There is perhaps no better example of this, though he might be reluctant himself to say so, than Keith Ford.
Governor signs loan forgiveness bill, vetoes paid maternity leave
From the Capitol – On the cusp of good things for part-timers
Budgetarily, it’s been a tough year for winning greater gains for part-timers in Sacramento, but with regard to legislation which CFT succeeded in getting to the governor’s desk, and for legislation already in the wings for next year, part-timers are on the edge of good things.
State Senator Adam Schiff goes to the head of the class
CFT Archive 1999
Most teachers speak with authority about the subjects they teach but Glendale Community College’s newest political science instructor speaks with the voice of personal experience as well. Adam Schiff knows the workings of California state government from the inside, as well he should — he’s Glendale’s state senator.
What I learned in my research of the “Involuntary Adjunct”
By Bobbi-Lee Smart, Cerritos Faculty Federation
My dissertation research focused on the perceptions of the impact of adjuncts on community college campuses in Southern California. I specifically wanted to understand the reality of involuntary adjuncts — those whose who want full-time tenure track jobs, couldn’t get a position, so worked as “full-time” adjuncts (those whose adjunct work is the majority or entirety of their income).
Freeway Flyers: Local action & quick news
Salary comparison, part-timer conference, celebrity part-timers
Los Angeles adjunct becomes chair of California Democratic Party
Rusty Hicks, known to the larger California public as the newly elected leader of the California Democratic Party, is known to the students of the Los Angeles Community College District and the Los Angeles College Faculty Guild, Local 1521, by another title since 2016 — Adjunct Instructor of Labor Studies.
Campus Equity Week highlights unjust working conditions for contingent faculty
Fund the Future by fighting for equity
It is not a level playing field in the world of higher education. The longstanding and systematic underfunding of higher ed has to a crisis in which 68 percent of California community college faculty now work as part-time, or temporary instructors.
California contingents unite to find “Common Ground”
In an event which channels the spirit of Campus Equity Week, leaders from the Peralta Federation of Teachers, San Mateo Community College Federation of Teachers, UC-AFT, and San Francisco State will host a free conference on the future of higher education at Berkeley City College on October 25.
AB 897: Raising the cap and reducing freeway flying
FIRST PERSON | By Geoff Johnson
The term “freeway flyer” has for years been synonymous with California part-time community college teachers. Since 1968, California part-timers have been legally restricted to teaching a faction of a full-time load in a given community college district, and then generally paid only for their instructional hours.
The rationale for this rule was that it allowed administrators more flexibility to deal with the drop in student sections from the fall to spring semesters, and at the same time, a way to get out of paying healthcare and retirement benefits.
- 1 of 3
- ››